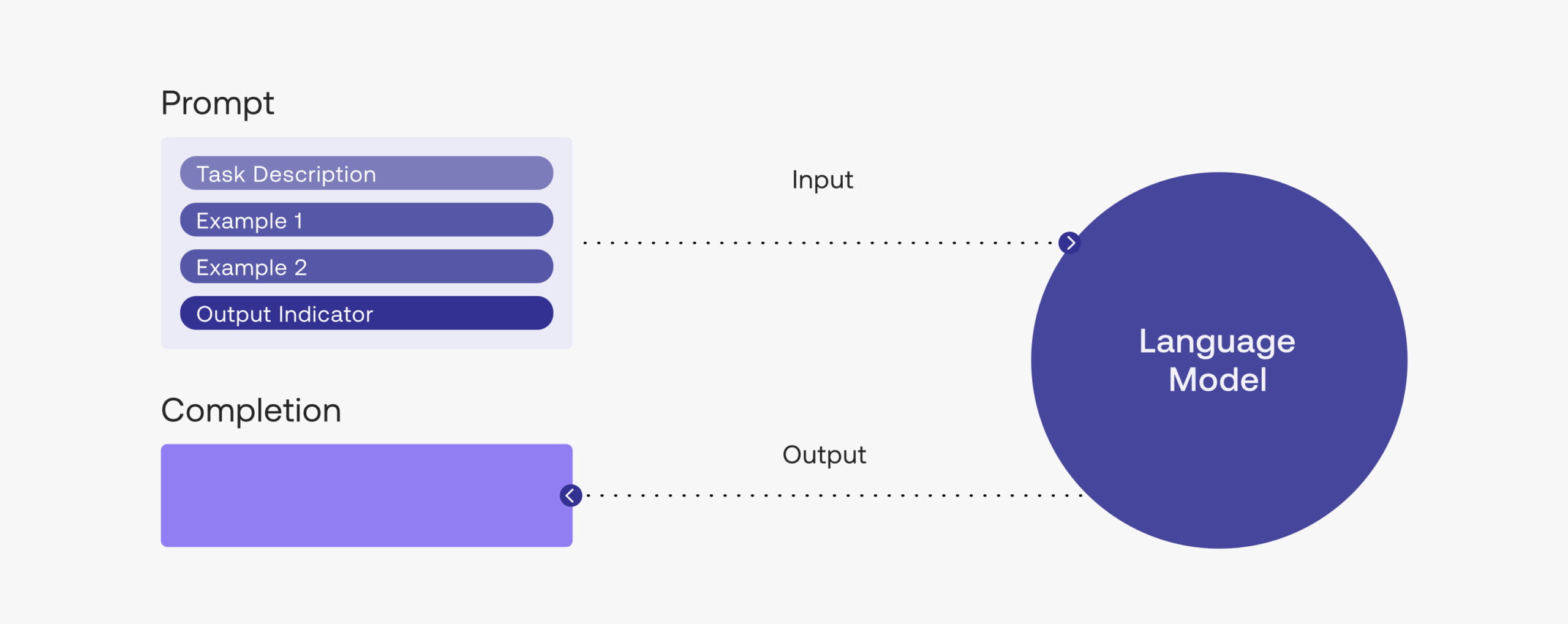
Basics of Prompting
LLM Settings
In Generative AI and Large Language Models (LLMs), like GPT-3.5, the ability to fine-tune and configure settings is key in shaping the outputs according to specific requirements.

To understand their impact on the model’s behavior, let’s explore these settings in detail.
Temperature
At its core, the temperature setting adjusts the level of predictability in the AI’s responses.
- Function: Temperature controls the randomness or predictability of the model’s output. A low
temperatureleads to more deterministic and predictable outputs, while a hightemperatureincreases creativity and diversity. - Application: For tasks requiring factual accuracy, such as fact-based QA, a lower temperature is ideal. Conversely, for creative tasks like poetry or story generation, a higher temperature might be more suitable.
- Example: Asking for a list of beach activities with a low temperature might result in conventional suggestions like swimming or sunbathing. A higher temperature might suggest imaginative activities like organizing a beach-themed treasure hunt.
Top P (Nucleus Sampling)
Top P, also known as Nucleus Sampling, is another fundamental setting in the operation of LLMs. By establishing a probability threshold, top_p ensures that only the tokens (words or phrases) that cumulatively exceed this threshold are considered for generating the response.
- Function: Top P is a method that controls the degree of randomness in the model’s outputs by setting a probability threshold. It focuses on a subset of the most likely next tokens.
- Application: A lower Top P is useful for more precise, factual content, while a higher Top P allows for more diverse and varied responses.
- Example: When completing a sentence, a low Top P might choose more common continuations, while a high Top P could result in unexpected or less common completions.
Max Length
The Max Length setting in LLMs determines the length of the output generated. This setting is a vital tool in controlling the verbosity or conciseness of the AI’s responses.
- Function: This setting determines the maximum number of tokens (words and characters) the model will generate in its response.
- Application: Useful for controlling the verbosity or brevity of responses. Setting a lower max length can keep responses concise, which is beneficial for summaries or brief answers.
- Example: In generating a story, a higher max length allows for more elaborate storytelling, whereas a shorter length will produce a succinct narrative.
Stop Sequences
Stop sequences are specific strings or phrases that instruct the AI when to halt its output generation.
- Function:
Stop sequencessignal the model to stop generating further content. - Application: It’s useful in defining the end point of a response, especially in structured formats like emails or lists.
- Example: Setting “Sincerely” as a stop sequence in an email ensures the model stops generating content before the closing salutation.
Frequency and Presence Penalties
Frequency and presence penalties are settings designed to reduce repetition in the AI’s outputs. The frequency penalty discourages the repeated use of specific tokens based on how often they have appeared in the text, promoting varied language use.
- Function: These settings reduce repetition in the generated text.
Frequency penaltyis proportional to the number of times a token appears, while presence penalty applies a flat penalty regardless of frequency. - Application: They are effective in enhancing the variety and richness of the content, preventing the model from overusing certain words or phrases.
- Example: In a descriptive paragraph, high penalties would prevent the repeated use of specific adjectives or phrases, encouraging more diverse language.
Determinism Note
- Even at zero settings for Temperature and Top P, outputs may not be exactly the same every time due to inherent randomness in the computational processes of the AI.
You should be aware that your results might differ according on the version of LLM you utilize before diving into some simple examples.